Physiology
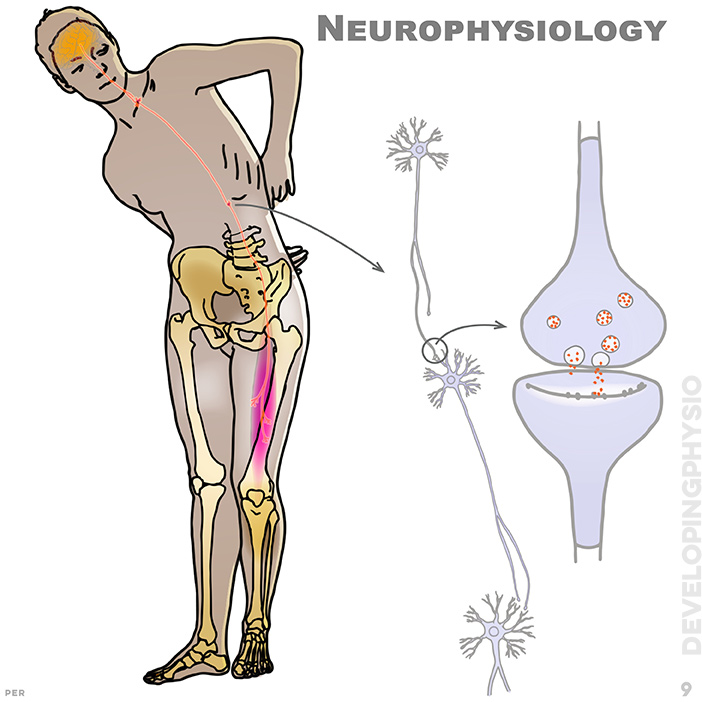
9. Neurophysiology: how brain and nerves work
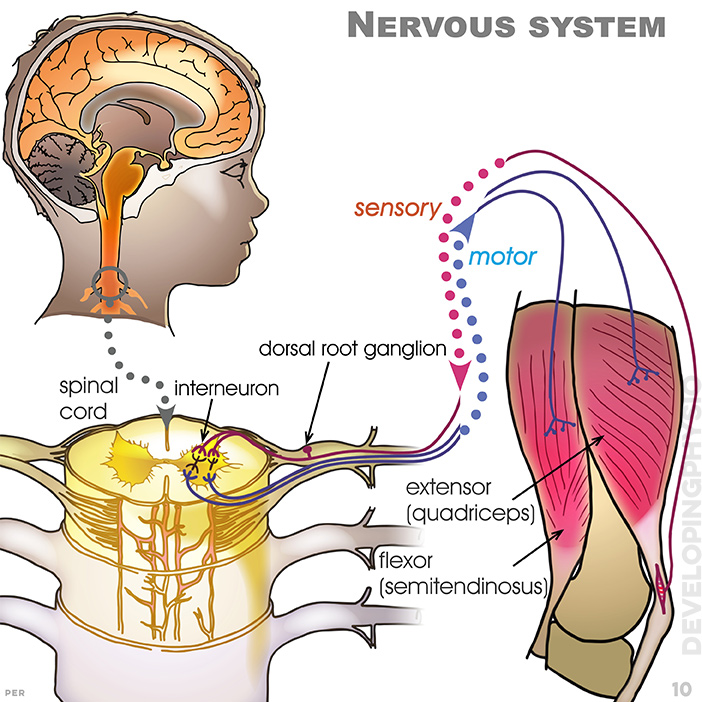
10. Nervous system: showing spinal cord; interneuron; dorsal root ganglion; sensory and motor systems
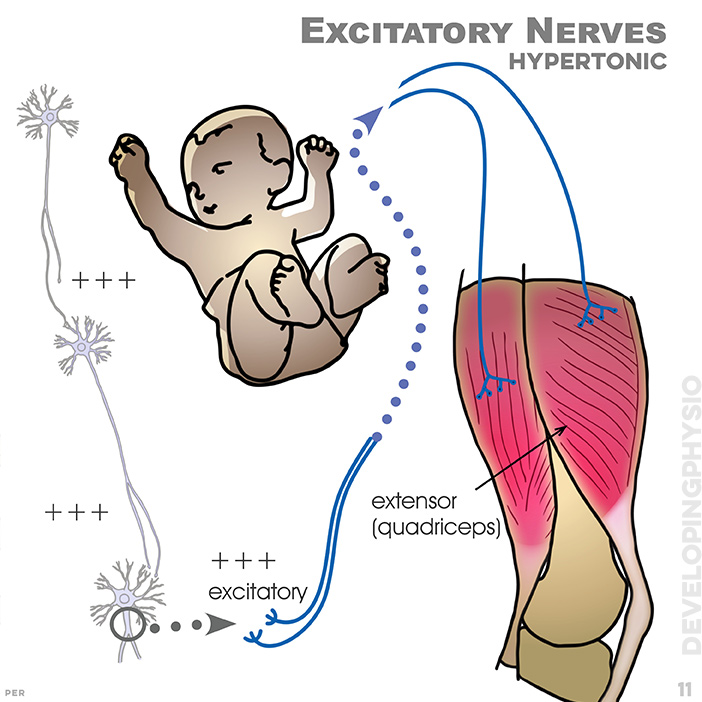
11. Excitatory Nerves, hypertonic: excitatory nervous patterns leading to high tone
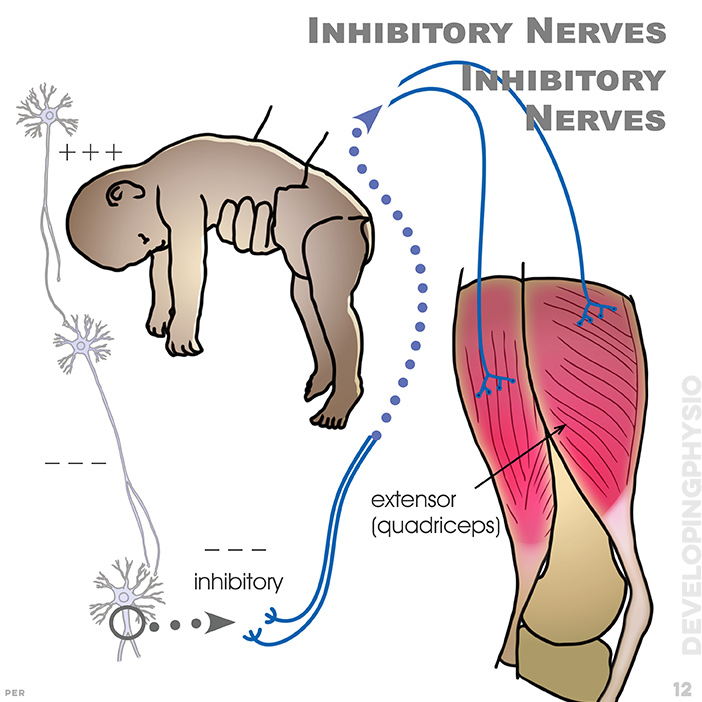
12. Inhibitory Nerves: stimulation of inhibitory nerve leads to reduced tone
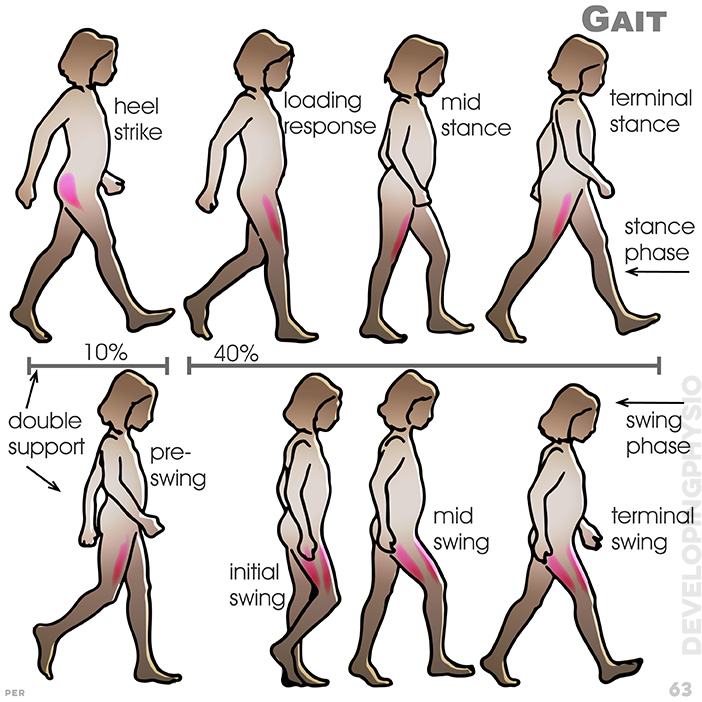
63. Gait. 1 Stance phase: heel strike; loading response; mid stance; terminal stance. 2 Swing phase: pre-swing; initial swing; mid swing; terminal swing
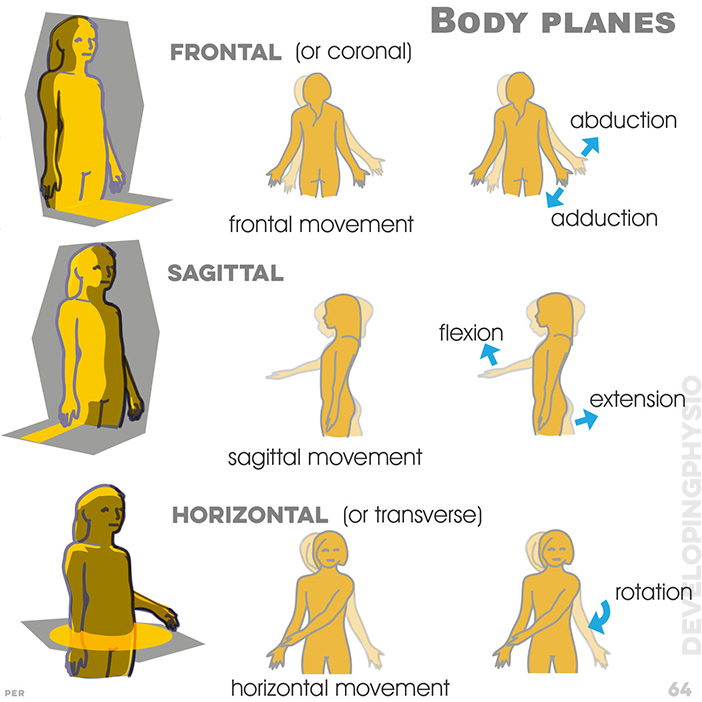
64. Body planes: frontal, frontal movement, abduction and adduction; Sagittal, sagittal movement, flexion, extension; Horizontal, horizontal movement, rotation
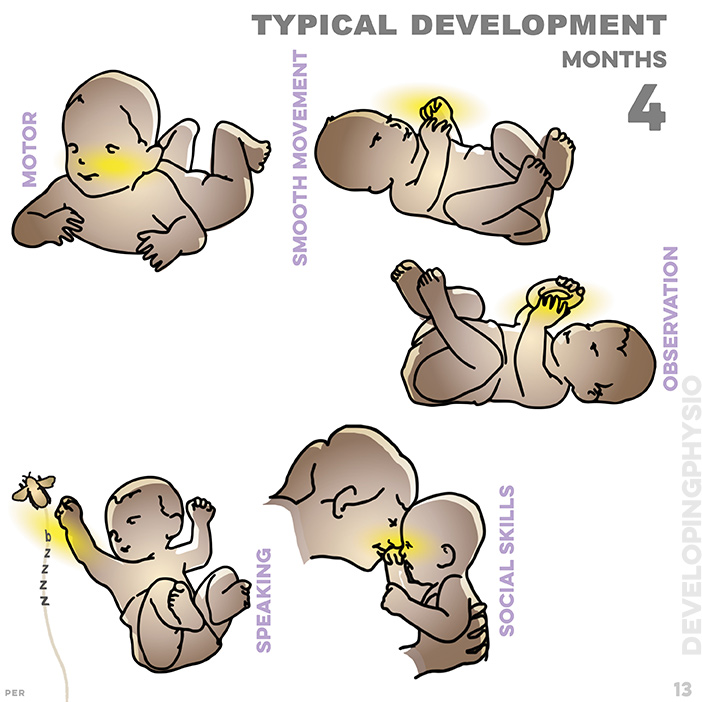
13. Developmental points between birth and 5 years old. typical development at four months in the following order: motor/ smooth development/ observation/ social skills/ speaking: Children with cerebral palsy will not match these, which can be a useful guide. these are: arms help to raise head; plays with both hands; able to observe toys; responds to sounds; smiles at mother
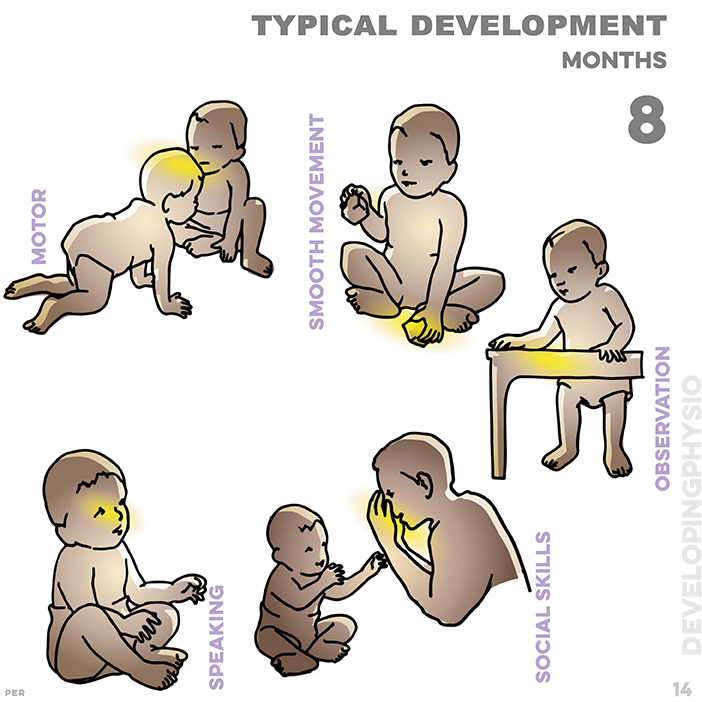
14. typical development at eight months: investigates unfamiliar briefly; grasps toy block with hand; pays attention, looks for toys; makes sounds: ma ma ta ta; capable of playing ‘boo’
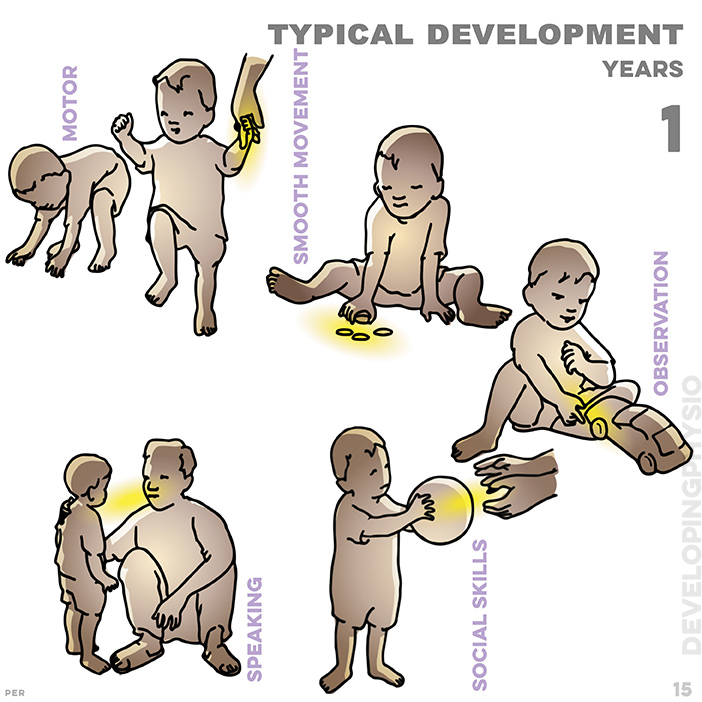
15. typical development at one year: stands alone, walks if held; pick up with thumb, forefinger; indicates ‘wheel’ ‘doll’ ‘eye’; 1 or 2 words, knows meaning; gives toy to parent
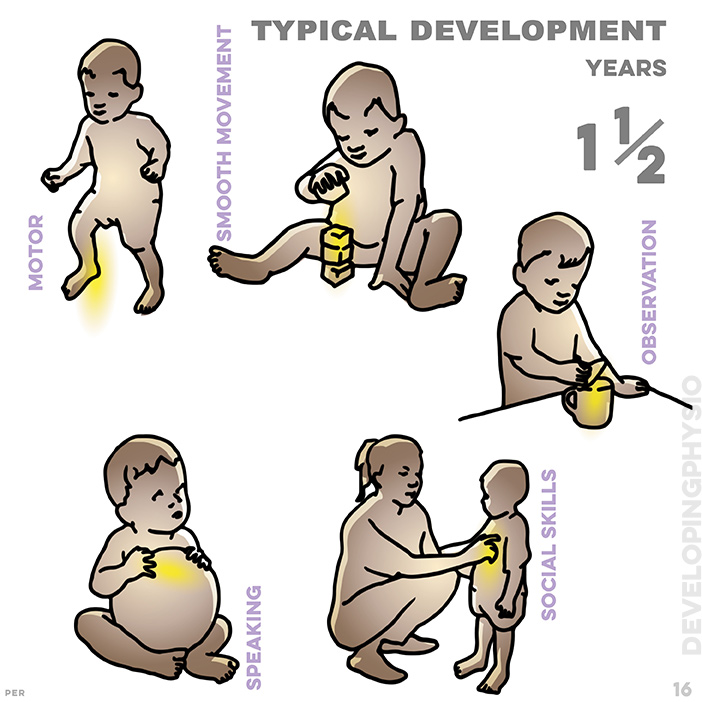
16. typical development and one and a half years: stands without falling; stacks three toy blocks; closes the lid; knows meaning of ten words; says own name if asked
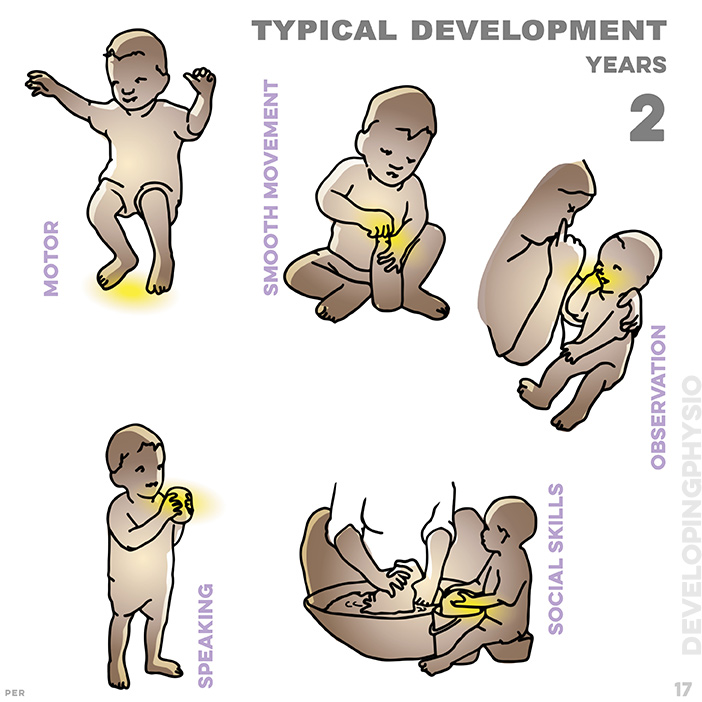
17. typical development at 2 years: jumps holding two people; turns lid to open bottle; names six parts of the body; answers in two word sentence; mimics activities of adults
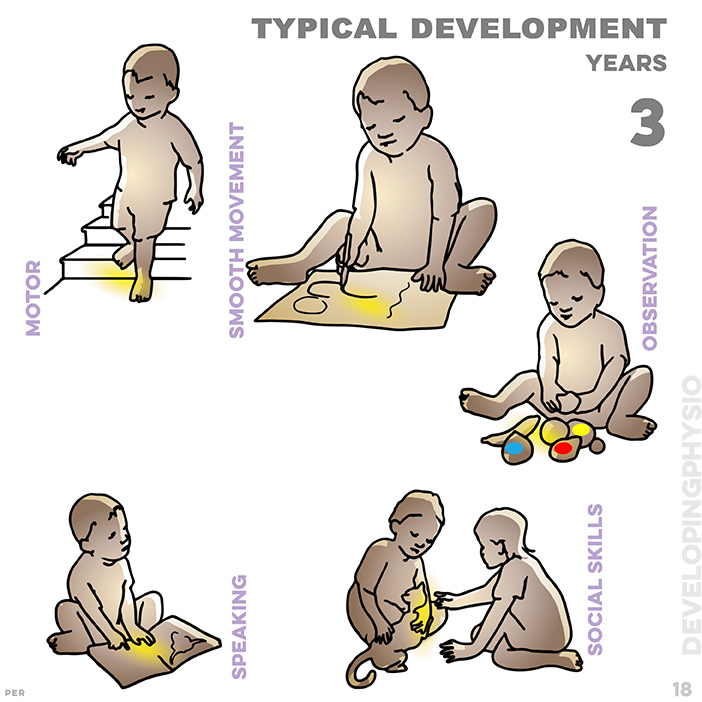
18. typical development at 3 years: descends stairs unaided; mimics lines and circles; can name three colours; uses ‘what, who, where?’; plays together with a friend
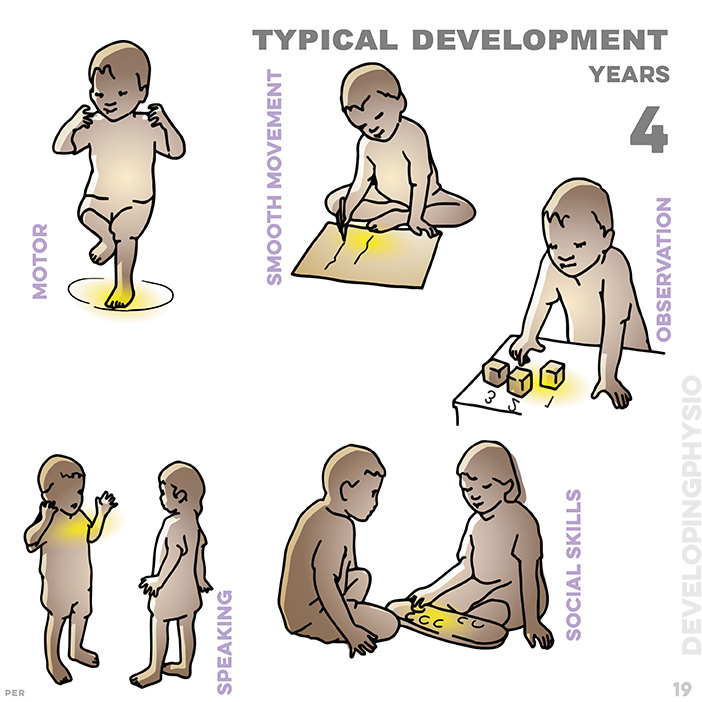
19. typical development at 4 years: holds pencil with fingertips; jumps with one foot; calculates three blocks; uses full sentences; plays games with friends
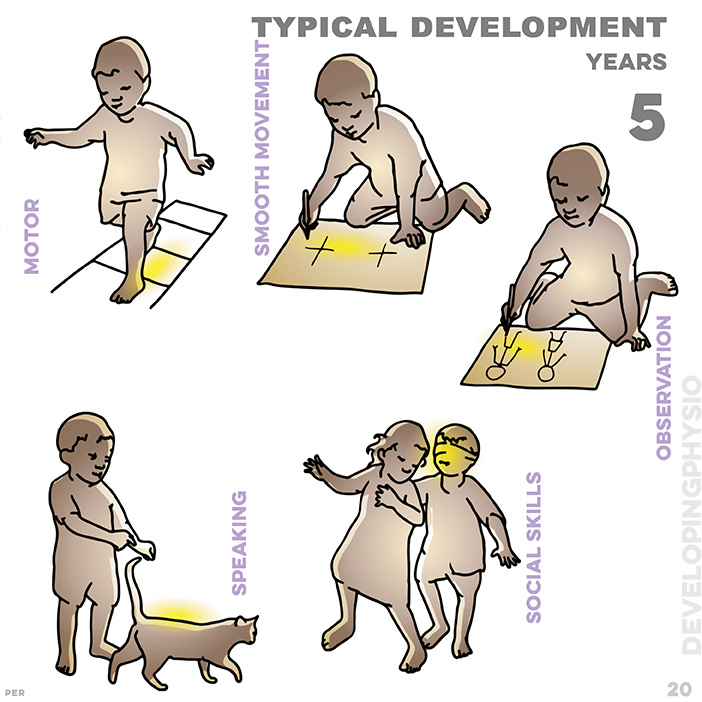
20. typical development 5 years: jumps on one foot forwards; mimics a sign; draws people; talks meaningfully; plays and follows game
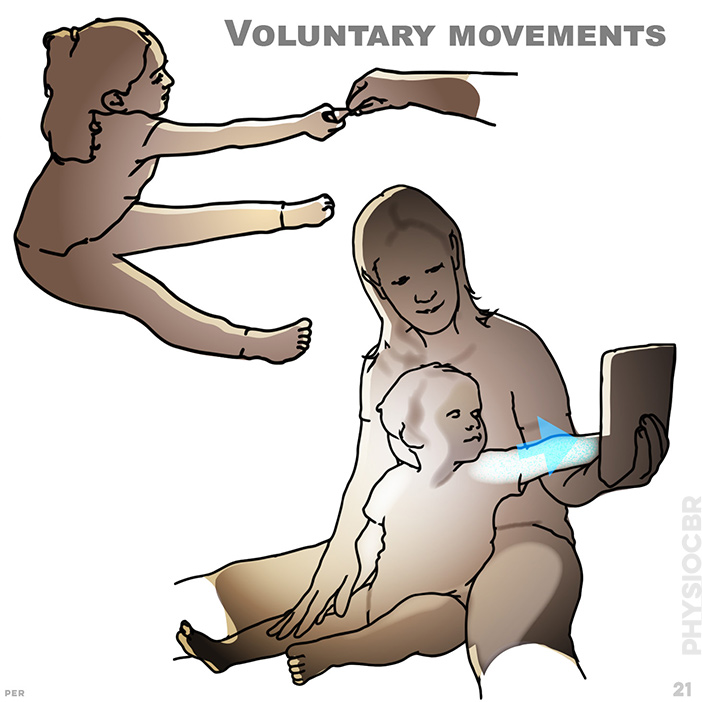

21. Voluntary movements: Voluntary movements strengthen automatic reflexes and motivating these through goal orientated play makes the effort fun
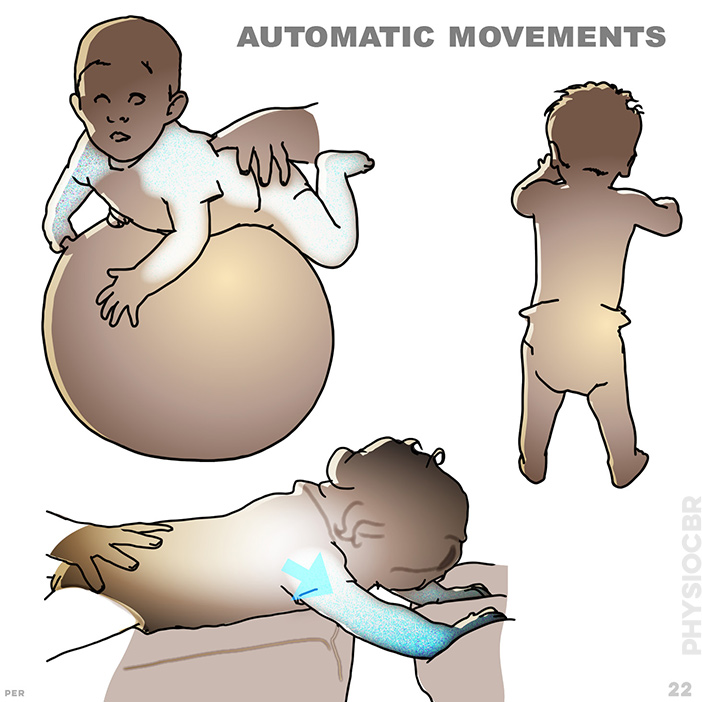
22. automatic movements: Automatic movements are largely unconscious, yet the vital patterns of muscle movements need encouragement
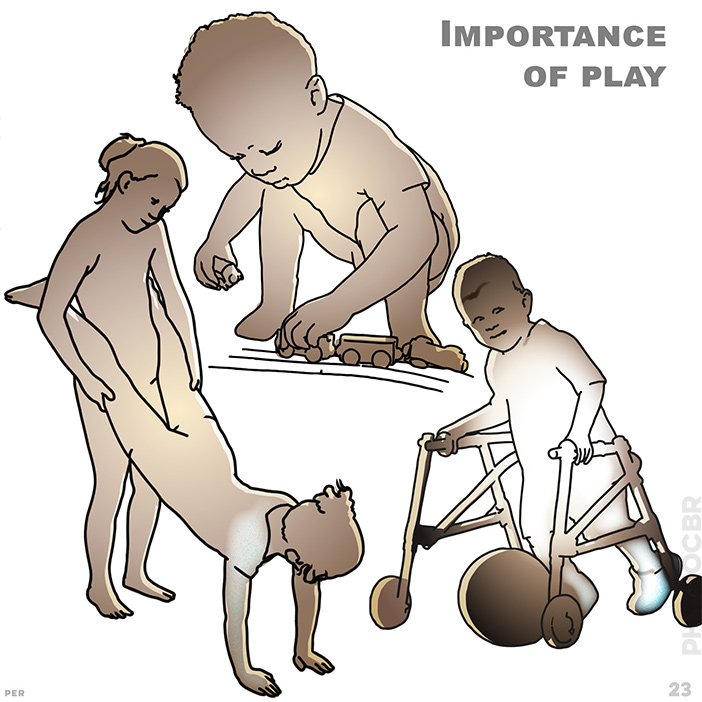
23. Importance of play: facilitating movement without the child needing to think about it engages co-operation whilst keeping things fun and full of play. showing: balance and reaction; ‘Wheelbarrow’ is a fun game that increases shoulder stability; kicking a football (even with a walking frame) helps weight transference
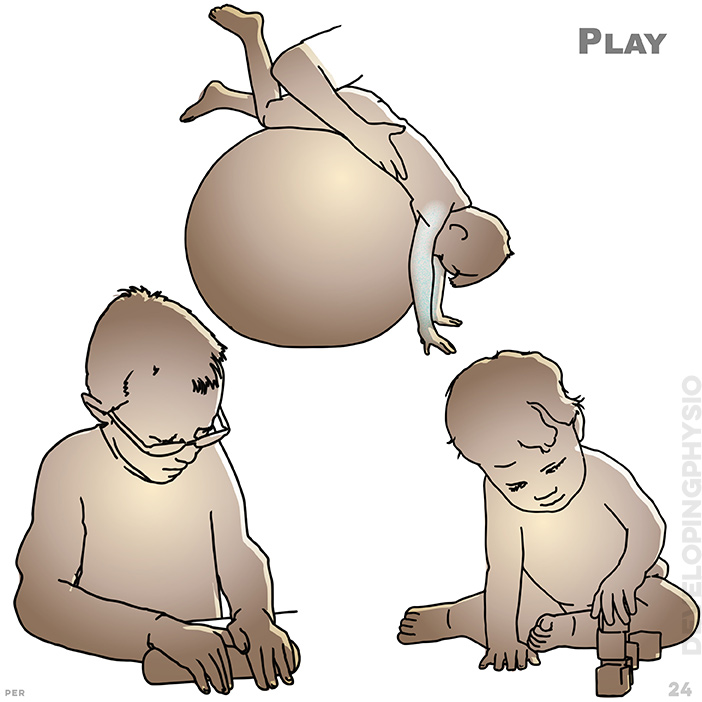
24. Play: An essential to all development, play provides life skills through such simple routines as feeding, dressing, and washing, as well as promote responses and awareness
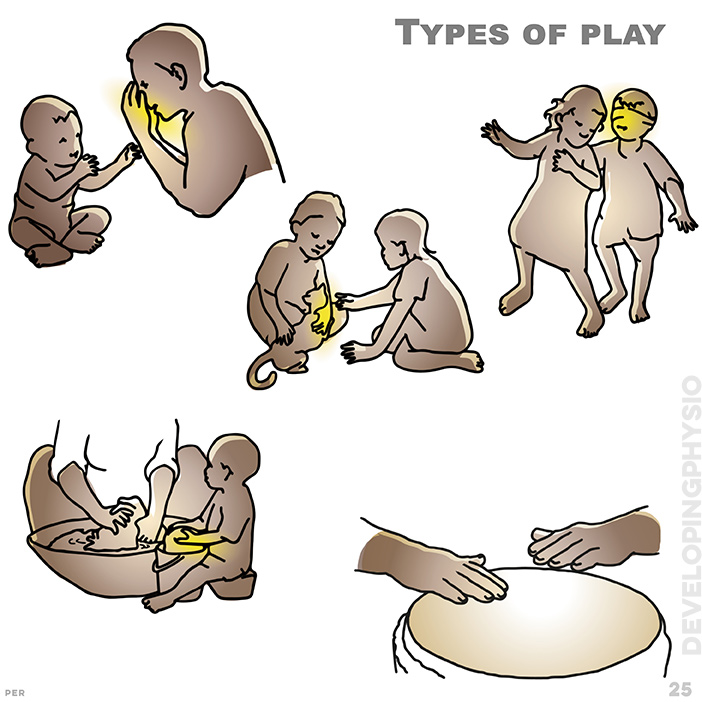
25. Types of play: Play is fun! Whether exploring, imitating, energetic, skilful, social, imaginative, interactive, pretence and role play, storytelling and reading... ALL are essential! typical play shown: explore (peek-a-boo); interact and amuse; energetic role play; imitate and ‘help’; communicate with skills
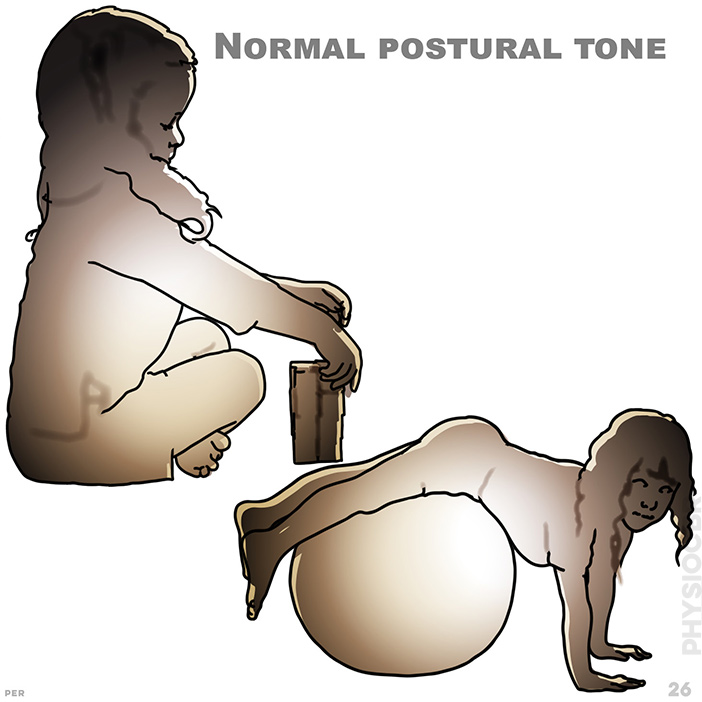
26. Normal postural tone: a wide variety of patterns and movement are included here, stimulating automatic response, balancing and protective reaction. smooth co-ordinated sequence of movement
The key phases:The STANCE followed by its SWING phase is normally an even and flowing rhythmn, yet it requires considerable muscle and nerve coordination. Clues to any underlying difficulty for a child can often be detected in their gait.
The key phases:The STANCE followed by its SWING phase is normally an even and flowing rhythmn, yet it requires considerable muscle and nerve coordination. Clues to any underlying difficulty for a child can often be detected in their gait.
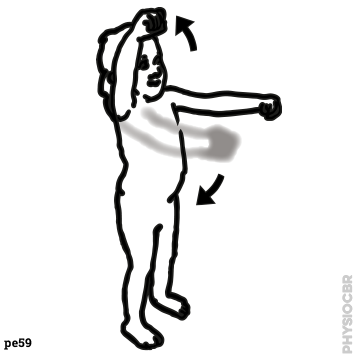
EXTERNAL ROTATION of arm moves it OUTWARDS around the body
INTERNAL ROTATION moves it INWARDS toward the body
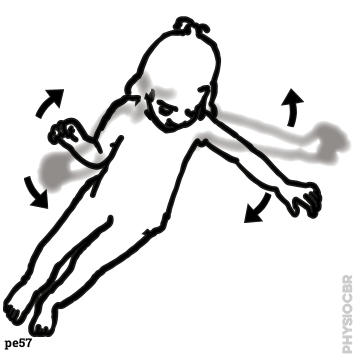
FLEXION means closing the
angle between any two parts, while
EXTENSION increases the angle between them.
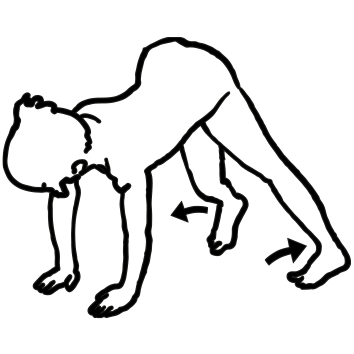
Arm ABDUCTION means moving away from the
body
ADDUCTION means movement back in toward it.